Search engine optimization (SEO) is the practice of using tools and methods to increase the quantity and/ or quality of traffic to a website organically (non-paid advertising). It’s not attempting to improve quantity or quality using paid ads that appear in search results.

There are an average of 6.5 billion web queries every day, and millions of websites, many of them competing for the attention of your prospects. To rank as high on the search engine results page as possible for terms related to your products and services — and the problems they solve — you need to master search engine optimization tactics. SEO is not a straightforward topic, which is why so many misconceptions have popped up over the years. Below are some we hear most often:
“Rank is all that matters.”
Although search rank will always be a measurement of success, it’s important to look beyond whether a website holds the first or second position on the search engine results page (SERP). Today it’s pretty common for two users to get completely different SERPs based on what they have previously searched for, and context in which they’re searching. Although rank can be a measure of success, it should not be the only one. Remember, too, that a good SEO strategy is about attracting people to your site; if your traffic is improving, you’re seeing success.
“My content can only have one topic.”
There’s nothing wrong with focusing on a niche vertical with your content, but all businesses should be open to including multiple broad topics. A larger content reach can tell Google that your site has broader appeal, with the result that more traffic is brought to your site. Even if you’re in a niche industry, there are connections to other related topics that potentially bring in additional qualified leads.
“I need to target high search volume keywords.”
Chunky middle and long tail keywords will yield more qualified traffic than short tail keywords which everyone is using. [As an example, by targeting the search term “whey protein ingredients for commercial dairy applications,” you will get more qualified traffic than by targeting the keywords “whey protein.”]
“I only need to do SEO for my website.”
Search engines weigh multiple sources on the internet, including social media platforms and online press releases, so optimization must be executed for everything you do online — videos, image alt tags, Twitter updates, etc.
“Search engines only search text content.”
Although the text on page is important, there are many other on-page factors that influence your search engine results page rankings. We will cover that more in depth in our On-Page SEO Chapter. Search Engine Optimization can be intimidating, even for people who have experience with it. In this guide our goal is to share key insights into what really affects your rankings and outline tactics any industrial manufacturer (any company, really) can implement. As you are reading this guide, if you get hung up on a term check out this dictionary.
“SEO can be done in a silo.”
SEO is viewed by some as a one-time event that can be outsourced. In fact, SEO involves every element of an inbound marketing strategy. Check out our infographic here for proof.
So, what exactly determines what appears in the number one position on a search engine results page? To answer that question, we’re going to assume that you’re using Google, since over 90% of the searches globally are done through this search engine.
Google’s search algorithm is what determines which website will be in the first position. Google continues to update its algorithm, optimizing it for the user’s experience (if you want to check out the full history of updates, MOZ has a great running list of algorithm updates). Organizations that play by the rules and focus on improving their SEO by following Google’s guidelines will improve their likelihood of being found by the right audiences – not just any searchers, but those who want the solutions you’re selling.
There will always be some tried-and-true components you need to work on when it comes to impacting your SEO. Luckily for us, SEMrush conducted research that identified what the factors are that determine search engine result page positions. Below are 17 of them, in order from most important to least important, that influence your SERP results:
Yes, there’s a lot to digest, which is why we’re going to take a look what each is and how to impact each with on-page or off-page SEO tactics.
On-page SEO opportunities revolve around the quality and quantity of the content on your site, and around how you utilize the keywords you want to rank for. These are what you have the most control over, and the easiest items to improve your SEO.
TIP: Google is now looking for answers to questions that users enter into the search engine, and keywords are just one part of this. Your writing must be informative and educational, not stuffed with keywords. Natural writing is seen as a plus to Google because readers value that content more than content that’s obviously written with Google in mind. A great example of this is the introduction of Snippets. A featured snippet is an “answer” selected by Google that best generally answers the searcher’s question; if he wants to learn more, he can choose to visit the source of that Snippet answer.
Before implementing an on-page SEO strategy, you’ll need to conduct keyword research to ensure you’re going after the keywords that will be the most impactful to your business.
Since Google’s Hummingbird update in 2013, the role of keywords in SEO has been reduced. Google no longer values individual sets of keywords entered in the metadata. Instead, the search engine places an emphasis on the content of each page.
Page titles and page descriptions are still important to Google, only because Google wants its searchers to have the best user experience. Instead of writing page titles and descriptions to cater to Google, write your page descriptions and page titles for the user. Google’s algorithm reads pages similar to how an actual person reads, and will penalize pages for keyword stuffing and awkward writing just to fit keywords in. You want to be descriptive and honest, but you still need to stand out.
The next step is to investigate how your website or blog ranks for specific keywords in the SERP for that particular search query. This technique will help clarify which keywords need to be targeted to rise in the page rankings. Using Google, it’s important to be logged out of any Google account when looking for the accurate SERP or if you are using Chrome you can use the incognito mode. When a Google user is logged in, SERPs change to reflect his or her past searches.
Another step to take is to make sure you have 301 redirects in place so you don’t receive 404 errors from any URLs that may no longer be in use. By using the 301 redirect, you redirect a majority of that link’s authority to the new one. It’s basically telling Google that the new link is replacing the old one.
These tips are the beginning of a keyword research strategy. By continuing to tune and adjust to new information, you’ll build a more targeted collection of keywords that will grow and shape your SEO strategy.
Keywords should still have a role in your SEO work, specifically for the on-page copy of your website. Unfortunately, Google has made keyword search data unavailable to users, making it more difficult to understand what people are searching; Google also eliminated its free Keyword Tool. But do not fear, there are other tools you can use to develop your keyword strategy.
Google
One place to gauge keyword traffic is the Google Keyword Planner. This free tool caters to pay-per-click (PPC) advertisers, but can still be utilized for organic keyword research. The Google Keyword Planner is similar to the previous Keyword Tool, showing a keyword’s monthly search volume, both globally and locally (local meaning U.S. searches). It also provides information on the competitiveness of the keyword (in relation to PPC campaigns) and Google’s recommended alternatives. Other tools you could use are SEMRush’s Keyword Magic Tool and MOZ’s Keyword Planner.
SEMrush
SEMrush can help you find new keyword opportunities, conduct backlink analysis and review competitors’ keyword information. It can also conduct site audits, position tracking (watches where you rank for certain keywords), and backlink analysis of your site.
MOZ
MOZ has some incredibly cool features including, but not limited to, open site explorer, keyword explorer, and link analysis. The tools MOZ offers focus on growing organic search through the content you create.
Bing
You can also utilize the keyword tool offered by Bing once you create an account. Bing’s tool is also for PPC campaigns but can be adapted for organic keyword research. The keyword data from Bing is usually similar to the results provided by Google, even though Bing uses a different search algorithm.
Whichever tool you go with is the one you should stick with. Bouncing between different keyword tools will muddle your results and have you running in circles. The varied keyword traffic numbers will be confusing, since each tool is sampling from different servers and algorithms.
The ultimate best practice in SEO today is strong content creation. Regardless of the impact of off-page techniques like consistent link-building and keyword maintenance, all search algorithms look for a foundation of high-quality, relevant content users can use to answer their questions.
Content aimed at optimization should follow four key principles:
Accelerating Improvements in Website Performance
Once they’ve established a content strategy, companies usually see a significant improvement in optimization and traffic. One of the key ways to ensure on-page content impacts SEO is to ensure that the website’s speed keeps up with the rest of the world’s fast pace.
Web users have become accustomed to web pages loading quickly. If pages don’t, people move on. Google understands this, so when its crawlers get held up dissecting a website’s content because of sluggish page load speed, search rank will suffer.
There are five content optimization techniques that help boost a site’s load speed:
Although there are a number of factors that go into SEO and SERPs, HubSpot is trying to help small and medium-size businesses (SMBs) conquer their SEO strategies by introducing a tool called Content Strategy. With Google prioritizing pages based on relevancy to the phrase/question that was in the search query, this tool is meant to help SMBs build their core content pages around their keywords and phrases.
But HubSpot knows that keywords are becoming more and more obsolete (which we have seen in recent Google algorithm updates) and that the true focus should be the general topics, not specific keywords, and introduced the concept of pillar pages to account for that fact.
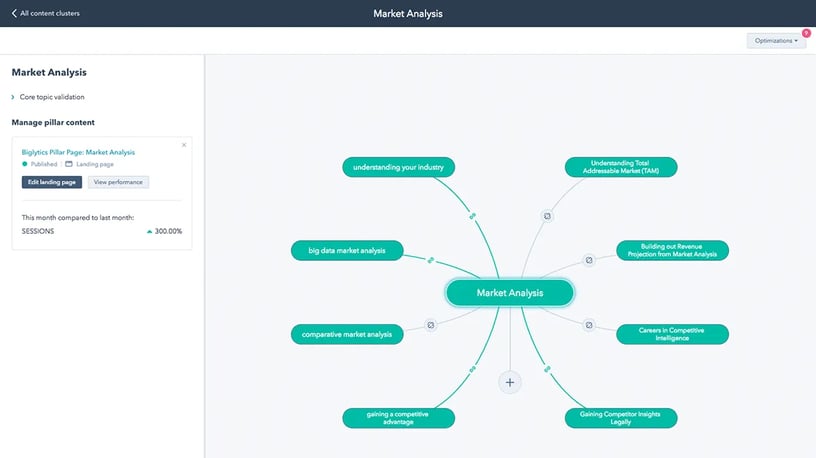
The pillar page is a long-form website page (more than 2,000 words, usually) addressing a specific topic. While the page is a solid resource in its own right, it also features links to related content housed throughout your site — other web pages, blog posts, and advanced content like eBooks and videos. Between the main content page and these linked resources, the topic is covered broadly in ways that are relevant to prospects.
Pillars (primary topics) and clusters (subtopics) are determined by knowledge/instinct and by metrics. Most businesses have a good sense of what their best prospects want/need to know about, and those make sense as pillar pages. But metrics should be used, too, because they’ll tell you what people are searching for, some of which you may not have guessed. HubSpot’s Content Strategy tool shows you the search volume of different terms, your domain authority related to those terms, relevancy and core topic similarity to that specific term. Check out Content Pillars and Topic Clusters 101 to learn more.
Off-page SEO is what impacts your search engine results the most. It’s also the most difficult to influence, since most of these factors are outside of your direct control. The biggest misconception is that off-page SEO is only about link building, but it’s much more than that.
What search engines are looking for in off-page SEO:
While every page on your website should be optimized by incorporating the right long-tail keyword phrases, this strategy accounts for just a small percentage of SERP performance. One of the biggest factors in SEO is having strong, reliable links. While your control over outside links is somewhat limited, there are six main link building principles that can boost a website’s page rank when applied correctly.
Keep in mind that not all links are created equal. There are good reasons directory links are only the first step — they are not nearly as valuable or as strong as social links built on good content. Links from media, trade associations, powerful brands, education sites or government sites are key to gaining great SERP rank quickly.
For many small or local industrial manufacturers, global domination of SERPs is not the goal. Instead, geography plays a large part in determining which customers they serve. On-page geographic SEO is about adding your region to metadata, page content and blog posts, and many businesses already use them well. However, to ensure a business is reaching the right audience within a specific target region, it’s important to have a localized link-building strategy in place.
Focused on a defined geographic scope, directory usage can provide the edge that will push you above others in the SERPs. Here are some tips for targeting a geographic area with directories:
We covered earlier in this ebook that backlinks are critical to SEO success, and leveraging social media links and reaching out to other high quality sources to receive backlinks will help your SEO immensely. This is why social media and public relations are critical in your SEO strategy.
Companies that ensure their websites, blogs, and landing pages are integrated with social media using social sharing buttons and other plugins are leveraging the impact of these signals to increase their relevancy and rank in search. Certain blogging platforms, such as the HubSpot blog platform, have built-in social sharing buttons and integration. Without that convenience, web managers have to do a little extra work. There are numerous social sharing plugins available, including some that have all the most popular social websites collected. The key is to offer sharing options on and off the content page, so that potential links and content awareness grow.
Public relations is social content. In this age of content marketing, public relations content is the kind of strong, reliable information that search engines love. PR content — news releases and stories — helps boost SEO results whether on the geographic, global, or virtual level.
News, by definition, can be anything new, unique, interesting or useful. That means it can be content about:
Any of those can be featured in a short press release that you publish on your website. Properly optimized and promoted via social media, PR is another opportunity to create new links and attract prospects to your website. Once a press release is published on the website, good promotion using social media tools is what differentiates today’s press releases from those of the past.
In addition to creating press releases, it’s also essential to start reaching out to credible sources (trade publications, industry associations, etc.) and asking them to put a relevant link in their content to yours. Maintaining and fostering these relationships with the gatekeepers of these sites is crucial to getting them to put you in the running for a backlink. You aren’t the only person with an SEO strategy who would want a backlink, and because they’re getting inundated with requests, known and trusted thought leaders will be the ones chosen to receive backlinks – so work on those relationships!
If you implement a comprehensive inbound strategy, you’ll be generating the authority and knowledge to showcase your company as an industry thought leader. This will give you or your inbound marketing agency all the content it needs to reach out to gatekeepers to start building those relationships.
Now that you know how to impact your SERP rankings with on-page and off-page SEO techniques, the next step is to understand how to measure success. Going back to the top factors that impact your ranking, the first four allow you to measure the success of the techniques you implement.
In addition to those four factors, below are metrics you can use as key performance indicators (KPIs) that will help you determine if you’re having SEO success.
Another key to understanding Google’s algorithm updates is to keep track of negative practices that you will be penalized for. Here are some of the most important things NOT to do:

Fill out the form on the right to download the SEO Survival Guide. You can print it, share it with friends and family or just use it as light reading when you’re on a plane! We hope you enjoy this eBook as much as we did creating it!